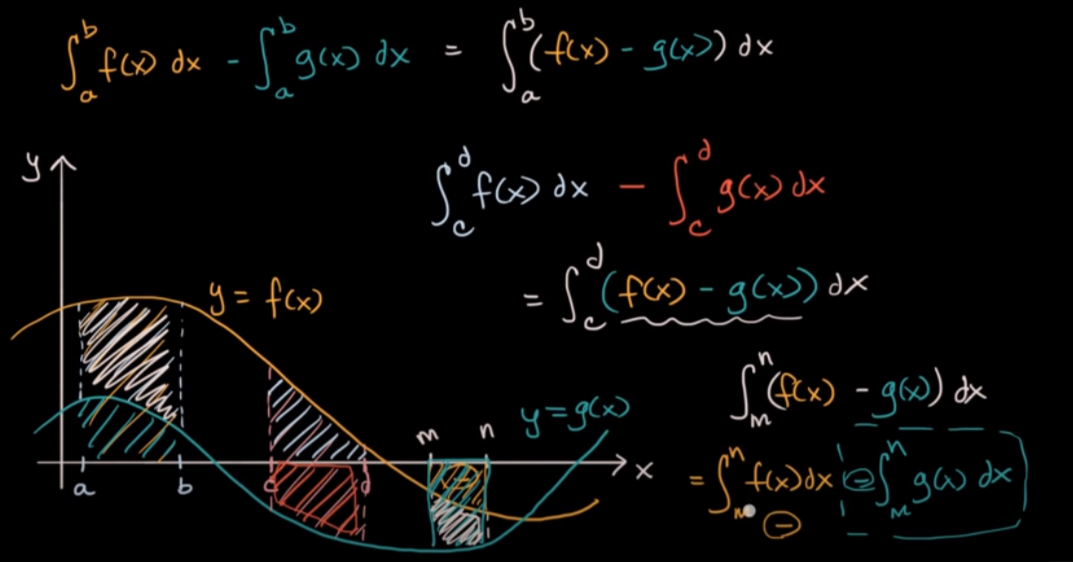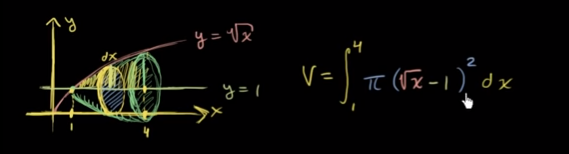Integrals
Summarize of derivatives and antiderivatives
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|
| F(x) | f(x) |
| |x| | |x|x/2 |
| Untitled | |
Differential equations
Applications of integrals - Average value of a function

Applications of integrals - Numerical integration
Limit
For any x, for any neighborhood N of f(x), there exists a neighborhood of x whose image is contained in N.
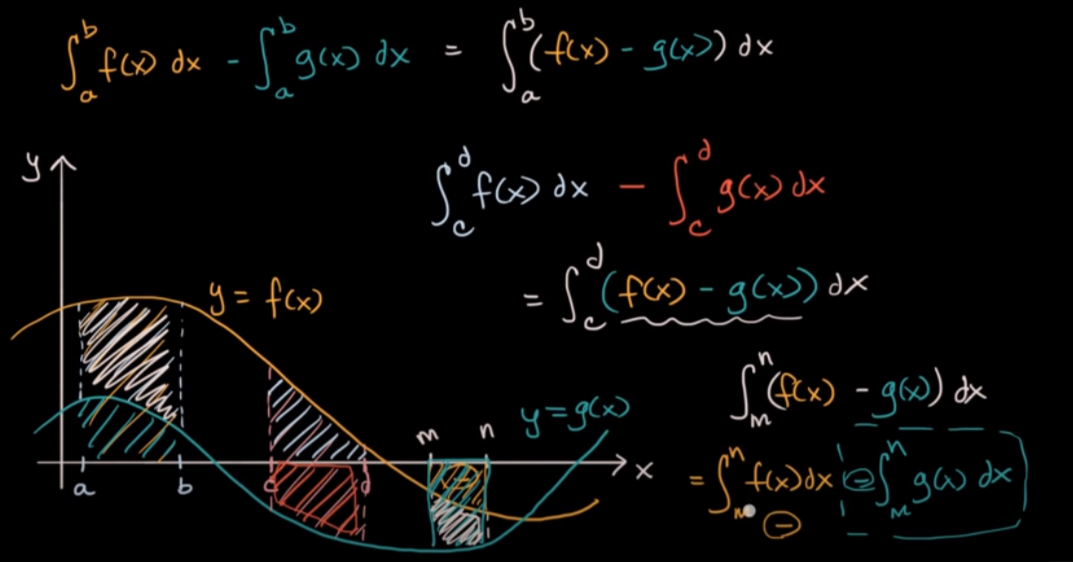
Area between curves
 Theory
TheoryPlanning.
∫ab∣h(x)∣dx≈6b−a[h(a)+4h(2a+b)+h(b)],where h(x)=f(x)-g(x) 
a,b are meetings of h, thus h(b)=0,h(a)=0 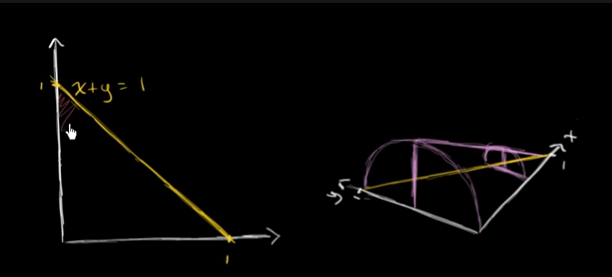 Worked example
Worked example

Volume with cross-sections
∫abA(h(x))dx,A(x) from shape problem
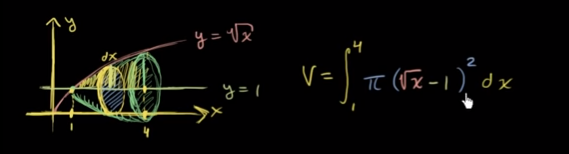
Worked examples
∫x1/ln(x)dx
x1/ln(x)=yln(x1/ln(x))=ln(y)ln(x)1ln(x)=ln(y)1=ln(y)y=e∫x1/ln(x)dx=ex+c
The volume of bodies of revolution
π∫ab∣f(x)−x′∣2dx π∫ab∣f−1(x)−y′∣2dx y-axis
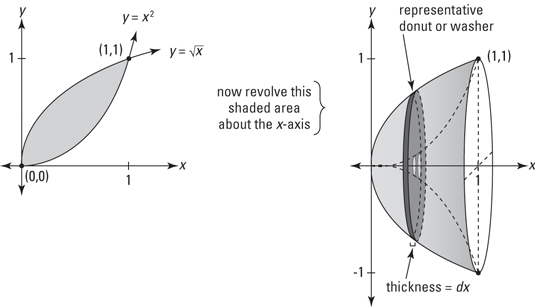
Solid of revolution between two functions
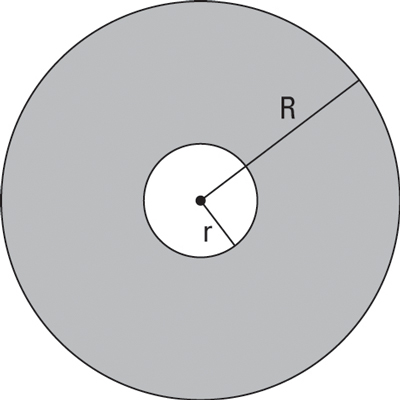
V=π∫ab∣(∣y′−f(x)∣)2−(∣y′−g(x))∣2∣dx
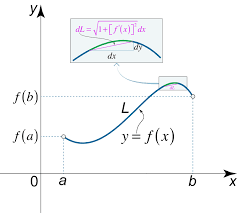
Arc length
L=∫ab1+f′(x)2
Euler Method
dxdy=F′(x); F(x0)=y0 yyou−want=ybefore+Δystep≈ybefore+y′Δx But, diferential equations are
dxdy=f(x,y)∣{y,y+1,x+4+y,...} Thus
dxdy=F′(x,y)=f(x,y); F(x0)=y0 y1=F(x1)=F(x0)+F′(x0,y0)Δx=y0+f(x0,y0)Δx y2(x)=y1+f(x1,y1)Δx yn+1=yn+f(xn,yn)Δx A good approx. step is Δx=0.00001, meaning that we need 400,000 steps (high computational cost).
Step sizes
| step size | result of Euler's method | error | Title |
|---|
| 1 | 16 | 38.6 | Untitled |
| 0.25 | 35.53 | 19.07 | Untitled |
| 0.1 | 45.26 | 9.34 | Untitled |
| 0.05 | 49.56 | 5.04 | Untitled |
| 0.025 | 51.98 | 2.62 | Untitled |
| 0.0125 | 53.26 | 1.34 | Untitled |
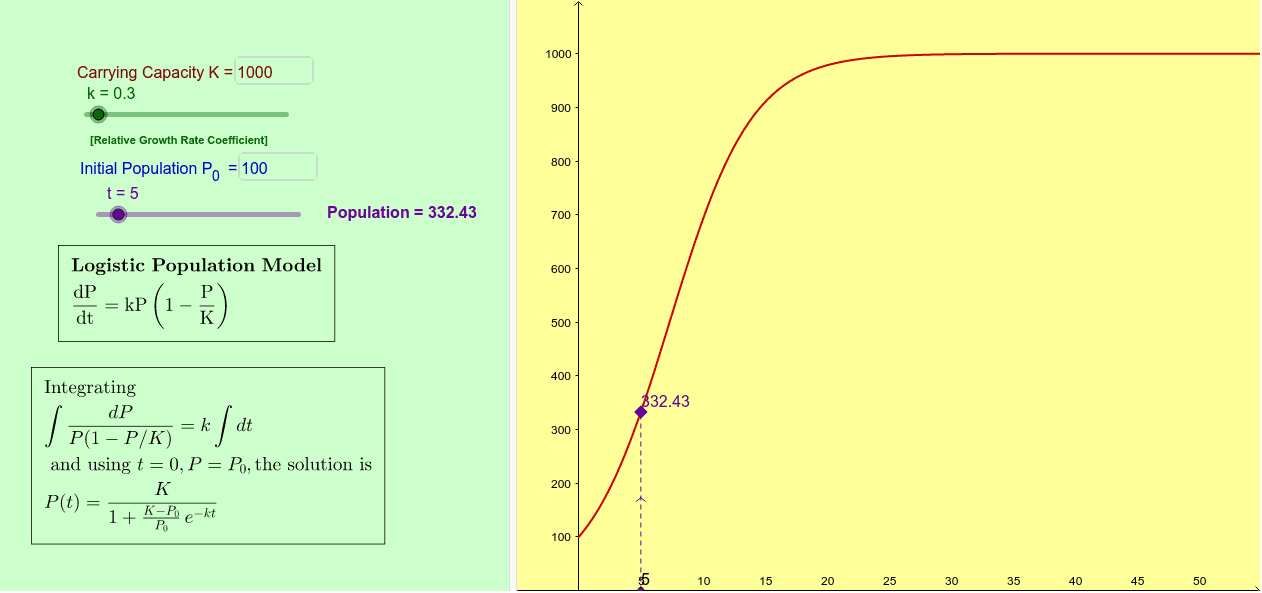
Logistic models
N(t)=N0ert,where N is the population. dtdN=rN(1−KN) https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Función_logística
Partial fractions
∫Q(x)P(x)=R0ln∣q0(x)∣+...+Rnln∣qn(x)∣ R=Q−1A−1b Q−1=1/q01/q1...1/qn A=[qnrn......q0r0] b=pn...p0 Example
∫(2x−1)(x+4)4x−11dx=R0ln∣2x−1∣+R1ln∣x+4∣[142−1][R0R1]=[4−11]R=[1/21][142−1]−1[4−11]=[−13]
Summation and series
https://www.cis.rit.edu/class/simg716/series_you_should_know.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_mathematical_series
Definition. Given a sequence a1,a2,...,an∈R,
Finite sum: k=1∑nak=a1+a2+...+an,n≥1k=1∑nak=0,n=0 But you can start with another index while exists in the sequence.
Examples.
Sequence={a0,a1,a2,...,an}k=0∑nak=a0+a1+a2+... Sequence={a}k=0∑1a=a+a Sequence={1,2,3}k=1∑3k=1+2+3
Properties
k=j∑nc=c(n−(j−1)),n≥j≥0 Linearity:k=1∑n(cak+bk)=ck=1∑nak+k=1∑nbk Arithmetic series: k=1∑nk=21n(n+1) Sum of squares: k=1∑nk2=6n(n+1)(2n+1) Sum of cubes: k=1∑nk3=4n2(n+1)2 Infinite sum: k=1∑∞ak=n→∞limk=1∑nak=n→∞limf(n) Geometric series:k=0∑nxk=1+x+x2+...+xn=x−1xn+1−1,x∈R−{0} Geometric series:
- A geometric series is a series in which the radio is constant.
- Common radio: anan+1
k=0∑∞xk=1−x1,∣x∣<1 Harmonic series: Hn=k=1∑nk1 Telescoping series: k=1∑n(ak−ak−1)=an−a0
Product
Definition. Given a sequence a1,a2,...,an∈R,
Finite product:k=1∏nak=a1a2a3...an,n≥1,k=1∏nak=1,n=0 Properties.
log2(k=1∏nak)=k=1∑nlog2(ak)
Bounding summations
Worked examples
∑k=1n(2k−1)
k=1∑n(2k−1)=2k=1∑nk−k=1∑n1=2(21n(n+1))−n=n(n+1)−n=n2
Show that ∑k=1n1/(2k−1)=ln(n)+O(1)
k=1∑n2k−11
Vector calculus
↗️Vector CalculusDifferential equations
📀Differential equationsReferences
https://calculusmadeeasy.org/
Complex analysis